AtaGenix Laboratories
AtaGenix Laboratories
Release time: 2025-08-25 View volume: 634
The spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2 is the major target of neutralizing antibodies and the basis of most vaccine strategies. Within its receptor-binding domain (RBD), the receptor-binding motif (RBM) directly contacts human ACE2 and is therefore a hotspot for protective immunity. However, the precise immunogenic epitopes and their corresponding protective antibodies in COVID-19 patients remained incompletely defined.
Researchers constructed two complementary phage display libraries: (1) an overlapping peptide library covering the entire spike protein, and (2) a single-chain variable fragment (ScFv) library from COVID-19 patient PBMCs. By screening with patient sera, they identified spike epitopes recognized by antibodies. Structural bioinformatics and ELISA validation were used to confirm immunogenicity, while neutralization assays and animal immunization tested functionality.
About 15 peptides across spike were recognized by patient sera, with three epitopes in the RBM (S431-454, S470-486, S501-515) showing the strongest reactivity. These regions are surface-exposed and divergent from SARS-CoV/MERS, indicating SARS-CoV-2 specificity.
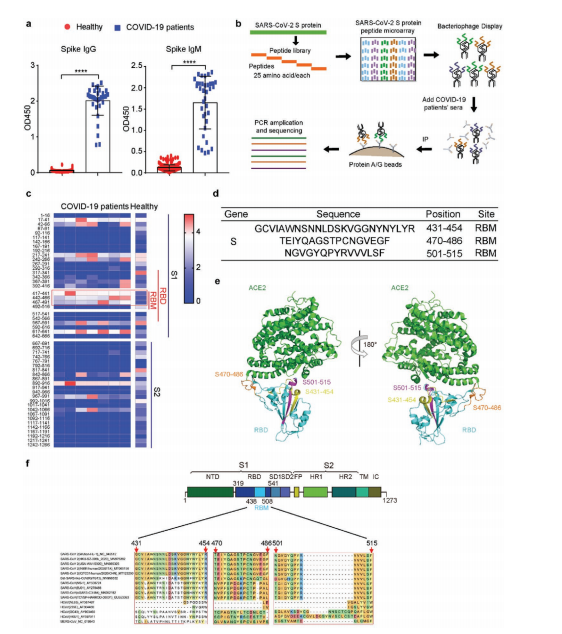
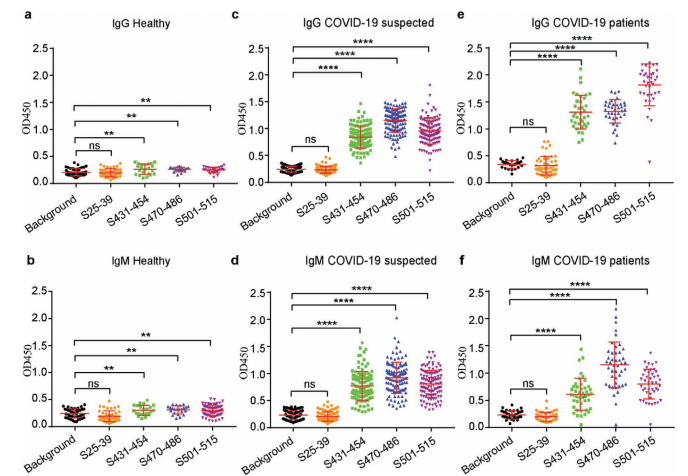
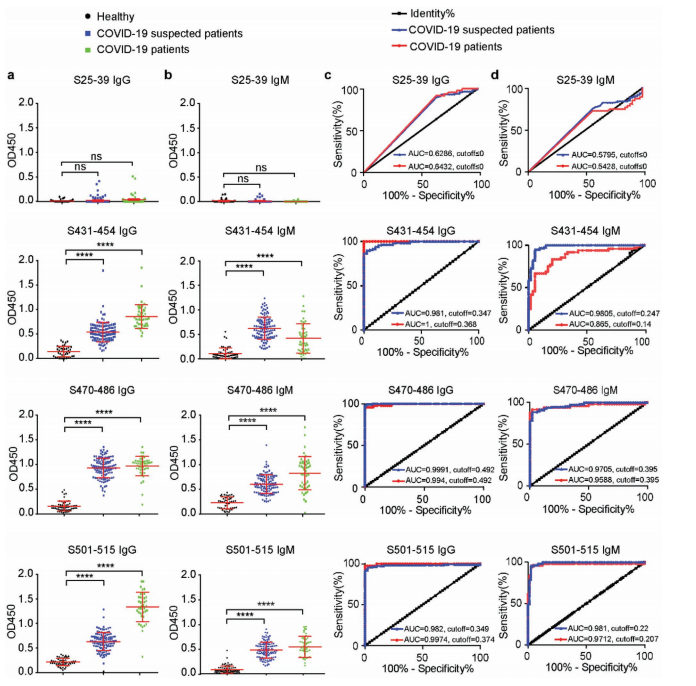
ELISA assays in 43 confirmed, 117 suspected, and 38 healthy individuals showed that antibodies against these three peptides—especially IgG—distinguished patients from controls with high sensitivity and specificity (AUC ~0.98–1.0).
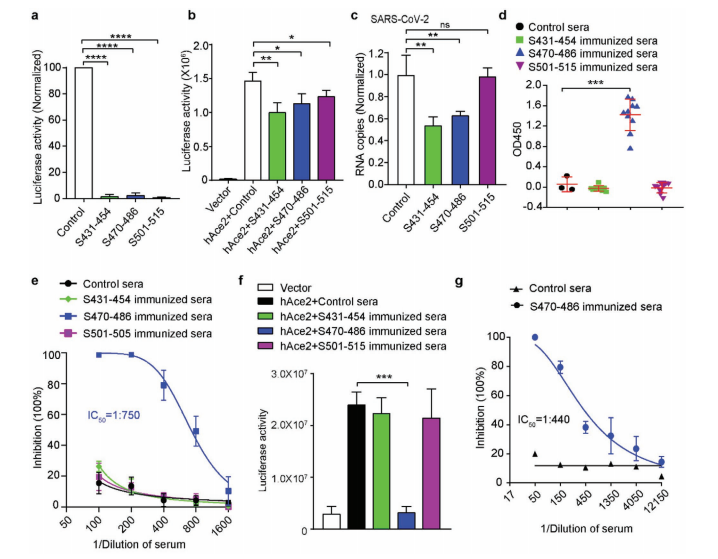
Synthetic peptides blocked pseudovirus infection in vitro, and mice immunized with S470-486—but not the other two peptides—generated neutralizing antibodies effective against authentic SARS-CoV-2. This established S470-486 as the most immunodominant epitope.
From a ScFv library of 8.7×109 clones, two monoclonal antibodies binding S470-486 were isolated. One clone (R3P1-F8) strongly neutralized both pseudovirus and authentic virus, demonstrating that functional mAbs can be rapidly obtained directly from patient repertoires.
The study combined phage display peptide mapping, ScFv library screening, structural modeling, and in vitro / in vivo validation assays. Notably, AtaGenix provided technical services in antibody library construction, phage display screening, and antibody expression, enabling the research team to rapidly obtain patient-derived monoclonal antibodies targeting the RBM epitope.
This study demonstrates a comprehensive workflow to map immunogenic epitopes, evaluate their diagnostic and protective potential, and isolate neutralizing antibodies directly from patients. The S470-486 epitope emerges as a particularly valuable target for diagnostic assays and antibody therapeutics. Importantly, AtaGenix’s antibody discovery platforms (phage display, ScFv libraries, CHO expression) were instrumental in validating these findings, underscoring how advanced CRO technologies accelerate translational immunology and therapeutic development.
AtaGenix provides integrated platforms to accelerate discovery from peptide to therapeutic:
Contact Us
+86-27-87001869
info@atagenix.com
Building C, R & D Building, No. 666, Shendun 4th Road, Donghu New Technology Development Zone, Wuhan

